|
|
 |
Suriname Travel Information and Hotel Discounts |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |

 |
|
|
●
Suriname Car Rental SuperSaver ●
 |
|
Major Listings Hotel Lodging
Accommodations in Suriname |
|
|

 |
|
Suriname
Hotel Accommodations |
|
Zeelandia Suites Hotel
PARAMARIBO
Walking Distance Of Casinos, The Pier,
Center Of The Capital. All Nine Comfortable Suites Consist Of A Living
Room, A Bedroom, A Balcony And A Bathroom. Every Suite Is
Furnished With Air Conditioning, Hot And Cold Running Water,
A Refrigerator, Cable Tv, Internet Facilities, And Telephone
With
Direct Access To International Lines. |
 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3D
Animated Flags--By 3DFlags.com |
Suriname
Find a premier Hotel & Resort at
Hilton Hotels.
or book Sheraton Hotels and Resorts
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The Republic of Suriname, more commonly
known as Suriname or Surinam, (formerly known as
Netherlands Guiana and Dutch Guiana) is a
country in northern South America, in between
French Guiana to the east and Guyana to the
west. The southern border is shared with Brazil
and the northern border is the Atlantic coast.
The most southern parts of the borders with
Guyana and French Guiana are disputed (upper
Corantijn and Marowijne rivers—the map shows the
Guyana and French Guiana versions of the
border).
History
Main article: History of Suriname
Though Dutch traders had established several
colonies in the Guyanas region before around
1600, the Dutch did not gain full control of
what is now Suriname until the Treaty of Breda,
which marked end of the Second Anglo-Dutch War.
After becoming an autonomous part of the Kingdom
of the Netherlands in 1954, independence was
granted in 1975. A military regime led by Dési
Bouterse ruled the country in the 1980s, until
democracy was re-established in 1988.
Geography
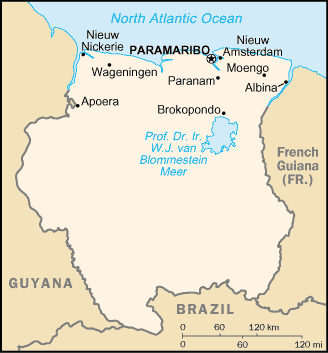
Map of SurinameMain article: Geography of
Suriname
Suriname is the smallest independent country in
South America. It is situated on the Guiana
Shield and part of Caribbean South America. The
country can be divided into two main geographic
regions. The northern, lowland coastal area
(roughly above the line
Albina-Paranam-Wageningen) has been cultivated,
and most of the population lives here. The
southern part consists of tropical rainforest
and sparsely inhabited savanna along the border
with Brazil, covering about 80% of Suriname's
land surface.
There are two main mountain ranges in Suriname:
the Bakhuil Mountains and the Van Asch Van Wijck
Mountains. Julianatop is the highest mountain in
the country at 1286 m above sea level. Other
mountains include Tafelberg (1026 m), Mount
Kasikasima (718 m), Goliathberg (358 m) and
Voltzberg (240 m).
Lying near the equator, Suriname has a tropical
climate, and temperatures do not vary a lot
throughout the year. The year has two wet
seasons, from December to early February and
from late April to mid-August.
Located in the northeast portion of the country
is the Professor Doctor Engineer W.J. van
Blommestein Meer, one of the largest reservoir
lakes in the world. It was created in 1964 by
the Afobakka dam (Brokopondo project), built to
provide hydro power for the bauxite industry
(which consumes about 75% of the output) and for
domestic consumption.
In the upper Coppename River watershed, the
Central Suriname Nature Reserve is a UNESCO
World Heritage Site cited for its unspoiled
rainforest biodiversity. There are many national
parks in the country: Galibi National Reserve,
Coppename Manding National Park and Wia Wia NR
along the coast, Brownsberg NR, Raleighvallen/Voltzeberg
NR, Tafelberg NR and Eilerts de Haan NP in the
centre and the Sipaliwani NR on the Brazilian
border. In all 12% of the country's land area
are national parks.
Demographics
Main article: Demographics of Suriname
Suriname's population of 438,144 (July 2005
est.) is made up of several distinct ethnic
groups. East Indians (known locally as
Hindustanis) form the largest group at 37 % of
the population. They are descendants of 19th
century immigrants from India. The Creoles,
mixed white and black, form about 31 %, while
the Javanese ("imported" from the former Dutch
East Indies) make up 15 %. Maroons (descendants
of escaped African slaves) make up 10 % and are
divided into five main groups: Aucans, Kwinti,
Matawi, Paramaccans and Saramaccans. Amerindians
form 3 % of the population (some say as low as 1
%), the main groups being the Akuriyo, Arawak,
Carib, Tirío and Wayana. The remainder is formed
by Chinese, Europeans, and Brazilian immigrant
workers that have arrived in Suriname in recent
times. A small Jewish community composed of
several families, descendants of Sephardim who
had earlier fled from Iberia to the Netherlands,
also inhabit the country. They previously
operated an autonomous region of Suriname called
the "Jodensavanne."
Because of the great number of ethnic groups in
the country, there is no one main religion. Most
of the Hindustani are Hindu, but Islam and
Christianity are also practised by them.
Christianity is dominant among Creoles and
Maroons.
Dutch is the official language of Suriname. The
Surinamese also speak their own languages:
Sranang Tongo (also known as Surinaams),
Javanese, Indonesian, and others. Also, the
original Carib and Arawak Amerindians of
Suriname speak their own languages, as do the
Maroons; Aucan (n'Djuga or Ndjukas) and
Saramaccan. Additionally, English and Spanish
are also widely used, especially at
tourist-oriented facilities or shops.
The vast majority of people (about 90%) live in
Paramaribo or on the coast. There is also a
significant Surinamese population in the
Netherlands.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Background:
|
Independence from
the Netherlands was granted in 1975. Five years later the
civilian government was replaced by a military regime that soon
declared a socialist republic. It continued to rule through a
succession of nominally civilian administrations until 1987,
when international pressure finally forced a democratic
election. In 1989, the military overthrew the civilian
government, but a democratically-elected government returned to
power in 1991. |
|
Location:
|
Northern South
America, bordering the North Atlantic Ocean, between French
Guiana and Guyana
|
|
Geographic coordinates:
|
4 00 N, 56 00 W
|
|
Map references:
|
South America
|
|
Area:
|
total:
163,270 sq km
land: 161,470 sq km
water: 1,800 sq km |
|
Area - comparative:
|
slightly larger
than Georgia |
|
Climate:
|
tropical;
moderated by trade winds |
|
Terrain:
|
mostly rolling
hills; narrow coastal plain with swamps |
|
Ethnic groups:
|
Hindustani (also
known locally as "East Indians"; their ancestors emigrated from
northern India in the latter part of the 19th century) 37%,
Creole (mixed white and black) 31%, Javanese 15%, "Maroons"
(their African ancestors were brought to the country in the 17th
and 18th centuries as slaves and escaped to the interior) 10%,
Amerindian 2%, Chinese 2%, white 1%, other 2% |
|
Religions:
|
Hindu 27.4%,
Muslim 19.6%, Roman Catholic 22.8%, Protestant 25.2%
(predominantly Moravian), indigenous beliefs 5% |
|
Languages:
|
Dutch (official),
English (widely spoken), Sranang Tongo (Surinamese, sometimes
called Taki-Taki, is native language of Creoles and much of the
younger population and is lingua franca among others),
Hindustani (a dialect of Hindi), Javanese |
|
Currency:
|
Surinamese
guilder (SRG) |
|
Currency code:
|
SRG |
|
Exchange rates:
|
Surinamese
guilders per US dollar - 2,178.50 (2001), 2,178.50 (2000),
987.50 (1999), 401.00 (1998), 401.00 (1997); note - yearend
rates
note: beginning in July 1994, the central bank midpoint
exchange rate was unified and became market determined; during
1998, the exchange rate splintered into four distinct rates; in
January 1999 the government floated the guilder, but
subsequently fixed it when the black-market rate plunged; the
government currently allows trading within a band of SRG 500
around the official rate |
|
|
Destination
Guides > South
America > Central
America & Caribbean |
|
|
|
|
|
|

